Wikipedia provides an interpretation: software requirements are a set of statements about the attributes, properties, or qualities of the software system to be implemented. Created in the process of developing requirements for software, as a result of requirements analysis.
Usually, the requirements refer to the system itself, its behaviour, qualities, structure, attributes, etc.
At the same time, business requirements are complex structured business goals for a particular organization or customers of the system. Business requirements explain why an organization needs this particular system and the goals that the business structure plans to implement with its help. Business requirements are not directly related to the implementation of the project as such but reflect the plans or intentions of the business.
What is the practical value of the requirements? They help to make any management processes more efficient by implementing certain models or standards. For example, automating the order creation process helps reduce time and simplifies order creation. And this, in turn, increases customer conversion, thereby increasing the efficiency of the business. So, business requirements are a highly effective tool that can work for the future and with perspective, But like any other tool, it must be used effectively, primarily due to the correct identification of requirements.
When talking about collecting and identifying requirements, I generally use the following sources:
- Internal knowledge and experience of the enterprise.
- Industry research and best practices.
- Regulatory documentation (laws and other legal acts, state standards).
- Analysis of competitors’ products.
Requirements identification is the process of communicating and collaborating with key stakeholders to accumulate vision and identify project needs.
Why are requirements identification important for project development teams, what are the necessary detection methods, and steps related to requirements identification? Let’s find out.
What is requirement detection?
Business intelligence uses data from key stakeholders to analyze and search for requirements to determine project needs, scope, assumptions, and risks. This is a mandatory part of requirements management, as the result affects the fundamental understanding of the project’s purpose. Failure to clearly define business needs can lead to project failure, which ultimately costs the client additional costs.
Requirements Discovery Process
An effective detection process is important because it provides the following benefits:
- The ability to reduce project costs by identifying problems with requirements even before development begins.
- Increase the likelihood that users and customers will get what they want. This significantly reduces the risk of project failure.
Taking into account best practices, there are five main stages of the requirements determination process:
-
Gathering information
By definition, “Gathering information” is the accumulation of data from disparate sources, while “extraction” is the act of obtaining information from a specific source. Both actions are essential to the overall requirement identification process and require experience to be properly implemented.
An effective way to prepare for the definition is to collect all available requirements by business analysts and study them to gain an understanding of the final result.
The findings obtained during the Gathering information of requirements will help identify key points of stakeholders and communicate which detection methods will best suit the essence of the project. Subsequently, business analysts join the process, accumulating experience that fills the absent requirements. Therefore, collecting requirements is an ideal first step in the process of updating them.
-
Identification of key stakeholders
As noted, the Gathering information of requirements can provide food for analysis for stakeholders. It is only important to identify the right people in advance so that everyone can start from one stage. This eliminates the need to fill in missing requirements later, which could potentially change the course of the project.
-
Getting demands from key stakeholders
There are many methods for identifying requirements. The Business Analysis Summary Guide from the IIBA International Institute (BABOK) names the main nine methods (brainstorming, document analysis, focus groups, interface analysis, interviews, observation, prototyping, requirements workshops, surveys/questionnaires), but that’s not all, such as protocol analysis, questionnaire development, etc.
The structure of the organization, the political climate, the nature of the project, as well as the personal preferences and preferences of the client greatly affect which methods are best suited for a particular task. Nevertheless, there are common methods that analysts of almost any experience or skill level can resort to, and which almost always provide high returns, namely:
No.1: Observation method
Surveillance is useful for capturing what has already been done and allows several other types of tools to be used for requirements, not the least of which are existing use cases. In addition, the analyst can document what he observes using UML diagrams and BPMN business process models, in addition to direct use cases in practice. This method not only helps the analyst to truly understand exactly what current business needs and processes are, but also provides access to a wide range of available diagrams and modelling methods, and ensures that the user can choose from this palette what suits him best.
No. 2: Brainstorming method
It has one but important advantage: you can avoid potential intermediate “tasks” on the way to the goal by involving other participants to help you better discover those goals that are already known. In addition, brainstorming allows you to get a lot of information at once, helping you understand the prospects of a project.
Conducted properly (uncensored by ideas along the way) and with the right audience (representatives of each group, SMEs, stakeholders), brainstorming has the greatest potential to prevent problems in the future by capturing needs you didn’t know you had, and brainstorming things that haven’t come to mind until now. To some extent, this relieves the manager of the burden of knowing their unknowns, helping everyone think outside the box and helping stakeholders take responsibility for a certain direction of the project
No. 3: Interview method
Advantage: By deeply exploring someone’s knowledge and needs one-on-one, you ensure that you understand a genuine, not just imagined, need.
Interviews will help you understand end users, what they understand and think, and whether this is what you need to prescribe stricter requirements. Interviews are an effective way to quickly collect large amounts of data, but its results, in particular the relevance and usefulness of the information collected, can vary significantly depending on the interviewer’s skills.
No. 4: Requirements workshops method
Advantage: you can quickly form the main requirements of the project.
A requirements workshop is a high-performance, focused event that brings together carefully selected key stakeholders and experts on a specific topic over a short intensive period (usually one or more days). But it should be remembered that the interested parties change their minds and add new experiences every six months.
No. 1: Prototyping method
The advantage: you can make sure that what you’re designing needs people, plus you still have time to change it.
Some people find it difficult to analyze a system or product until they try it in practice. But this way of perception is not always possible to implement in practice. Prototyping cannot be done at a very early stage of the project – so some idea of the ultimate goal of the task is required before starting the process.
The advantage of using prototypes is that they encourage stakeholders, or rather users, to play an active role in requirements development. This technique is extremely useful in the development of new systems. There is also software that allows you to make prototyping available to analysts.
-
Requirements for documenting requirements
An important step in the process of identifying claims is documenting them obtained so far. There are various formats for documenting requirements, but the best tool for documenting requirements depends on the project because it should be convenient for the entire project team.
Documenting claims is also important because using the wrong documentation tool for work can be harmful. Spreadsheets or local requirement files can work for short projects. Complex projects, on the other hand, benefit greatly from requirements management software, which can optimize requirements definition and overall process with features such as real-time tracking and compliance management.
-
Confirmation of findings
Once business analysts document requirements, you need to make sure they are written correctly. Requirements are sent to all stakeholders for review so that there is a collective understanding of what is being developed. Stakeholders are likely to clarify. It is also possible that this step will trigger additional requirements that will require review before being approved.
Business analysts conduct the process of determining requirements at the beginning of a project, but this point continues throughout the development process. This is because changes always happen and it is impossible to know all the questions you need to ask or get all the right answers in advance.
Problems of successful requirements detection
The detection process may seem simple, but it is not such a primitive task given the long-term or complex projects. One of the most common problems in the process of determining requirements is changing the requirements themselves for project implementation. Priorities shift and problems arise – therefore, it is best to plan changes. Be sure to establish a process that allows time to resolve issues, document changes and add new requirements, and conduct additional checks.
Summary
Effective identifying requirements is a combination of art and science for business analysts. They need to know what questions to ask and how to ask them. In addition, business analysts must be able to communicate and collaborate with key stakeholders at all stages of the discovery process.
Business analysts working on complex or regulated projects cannot rely on Word files or spreadsheets to document requirements. The level of difficulty at which they work requires that they have the best requirements detection tools on hand.
That is why in a complex, rapidly changing modern world, a modern way of requirements management using BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), which is the best way to visualize business processes, is gaining popularity. This business process modelling language is an intermediate link between visualization and implementation of a business process. With the help of modelling, we can describe any business processes, and they can be executed in various management systems, thereby speeding up the quality of interaction and returns between processing, customers and the product.
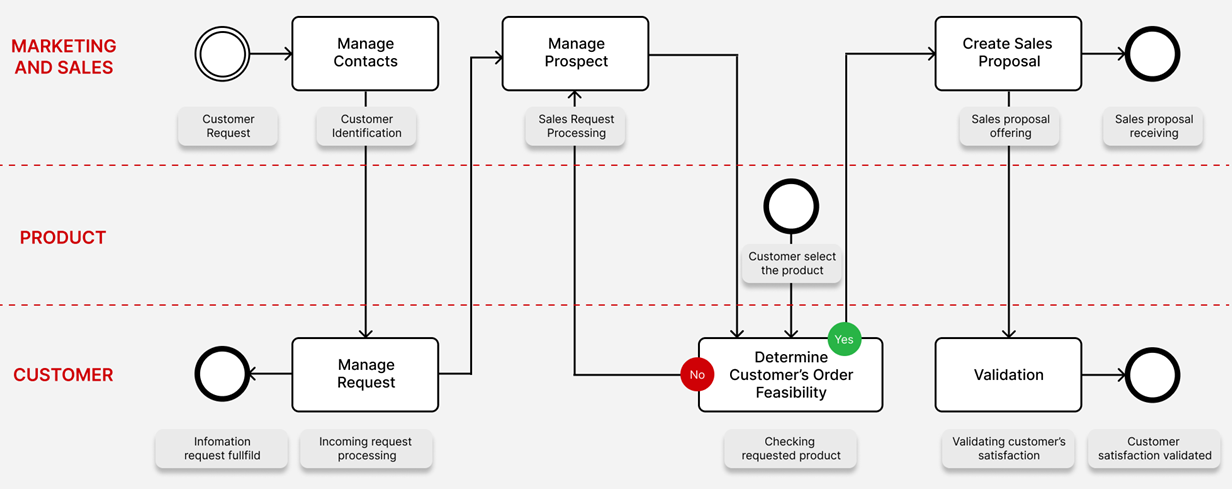
BPMN does not describe IT systems in general. This notation is intended to describe a specific subject area of a real business. A variety of components can be involved here: both software systems and living people (company employees, customers, suppliers). This distinguishes notation from graphical means of describing programs.


